本网讯 近期,我校先进土木工程材料科研团队杨军博士联合武汉理工大学,在混凝土材料水化产物组成和C-A-S-H凝胶微结构研究领域取得新成果,在国际知名建筑材料期刊《Construction and Building Materials》(中科院1区,影响因子7.693)上发表了题为“Effect of Sulfate Attack on The Composition and Micro-mechanical Properties of C-A-S-H Gel in Cement-slag Paste: A Combined Study of Nanoindentation and SEM-EDS”的研究论文(https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2022.128275), 杨军博士为第一作者,武汉理工大学产学研首席教授/金沙体育讲席教授丁庆军和我校张高展教授为共同通讯作者。

此科研成果采用纳米压痕测试结合SEM-EDS方法,研究了外界硫酸盐侵蚀条件混凝土材料中C-(A-)S-H的力学纳米结构转变规律和性能劣化机理,提出硫酸盐侵蚀引起的C-A-S-H凝胶脱钙脱铝过程中孔隙率增加是其微观力学性能下降的原因,研究成果丰富了对于严酷环境下硫酸盐侵蚀C-(A-)S-H凝胶微结构和性能演变机理的认识。
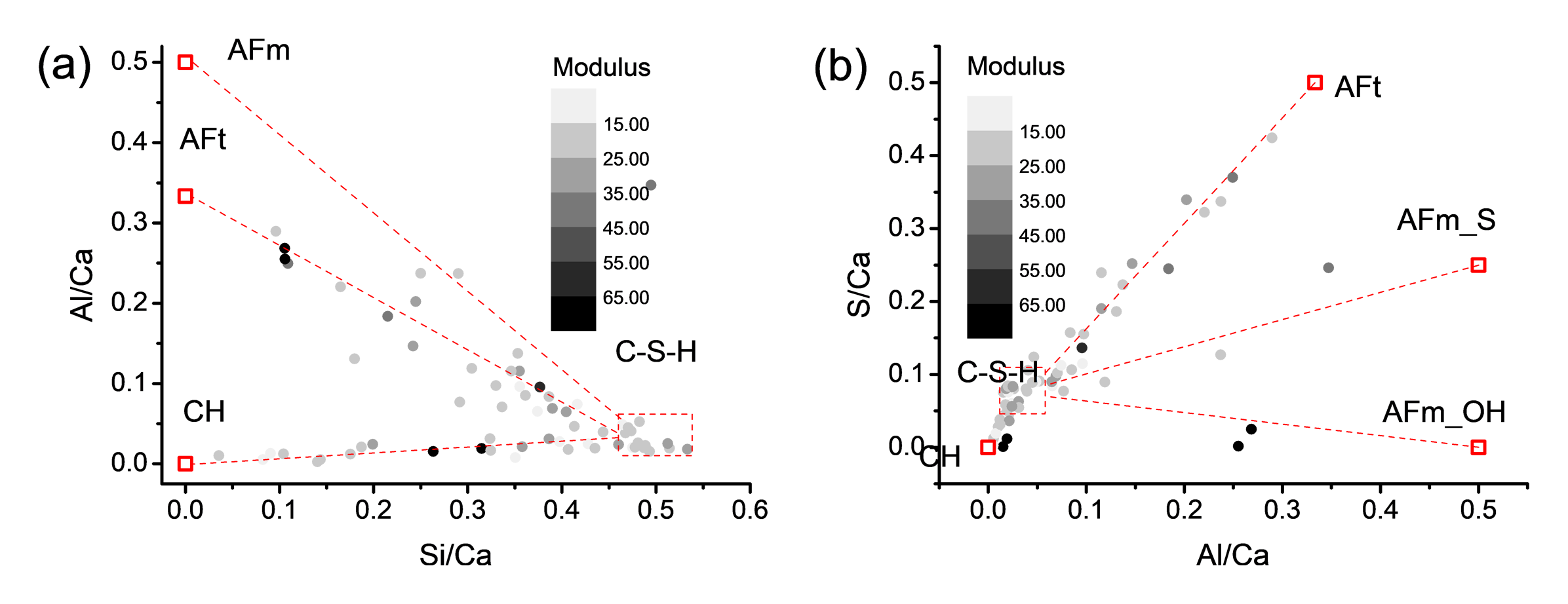
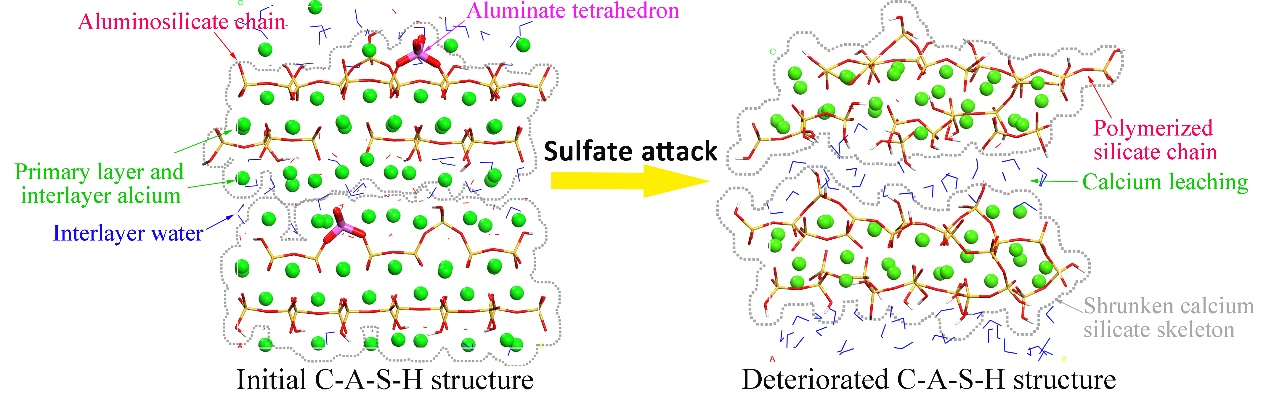
Fig. Schematic illustration of the nanostructure deterioration in C-A-S-H induced by sulfate attack
这也是杨军博士联合青岛理工大学侯东帅教授在《Construction and Building Materials》发表的题为“Structure, dynamics and mechanical properties evolution of calcium silicate hydrate induced by dehydration and dehydroxylation” (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.123327)的高水平论文之后的又一项重要成果。

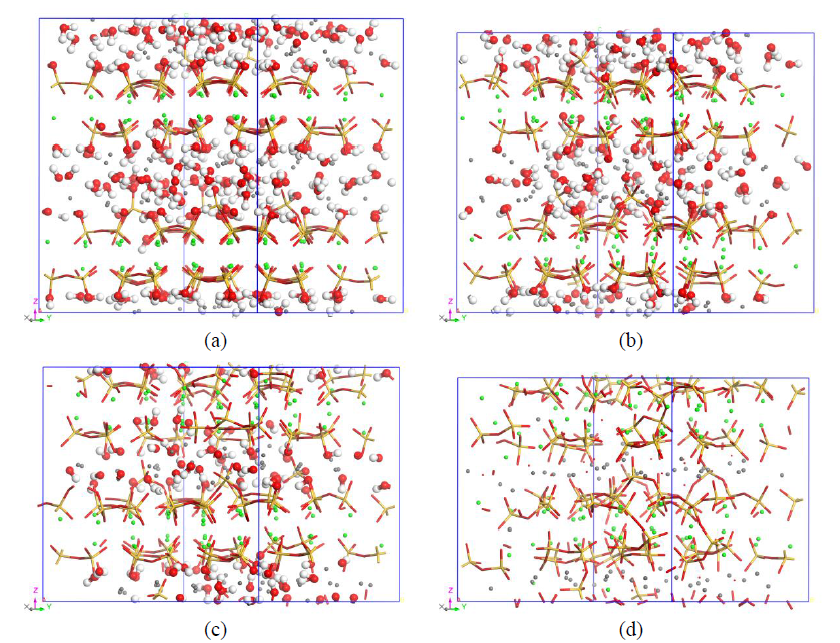
Figure 2. Molecular structures of the C-S(-H) with hydration degree of (a) 100%, (b) 60%, (c) 30% and (d) 0%. The molecular structures for all the models are presented in Supporting Information. (Yellow and red sticks represent the Si-O bonds; red and white ball-sticks represent hydroxyls and water molecules; green and gray spheres are calcium atoms in principal layers and interlayer regions, respectively; red points denote ionic oxygen atoms)
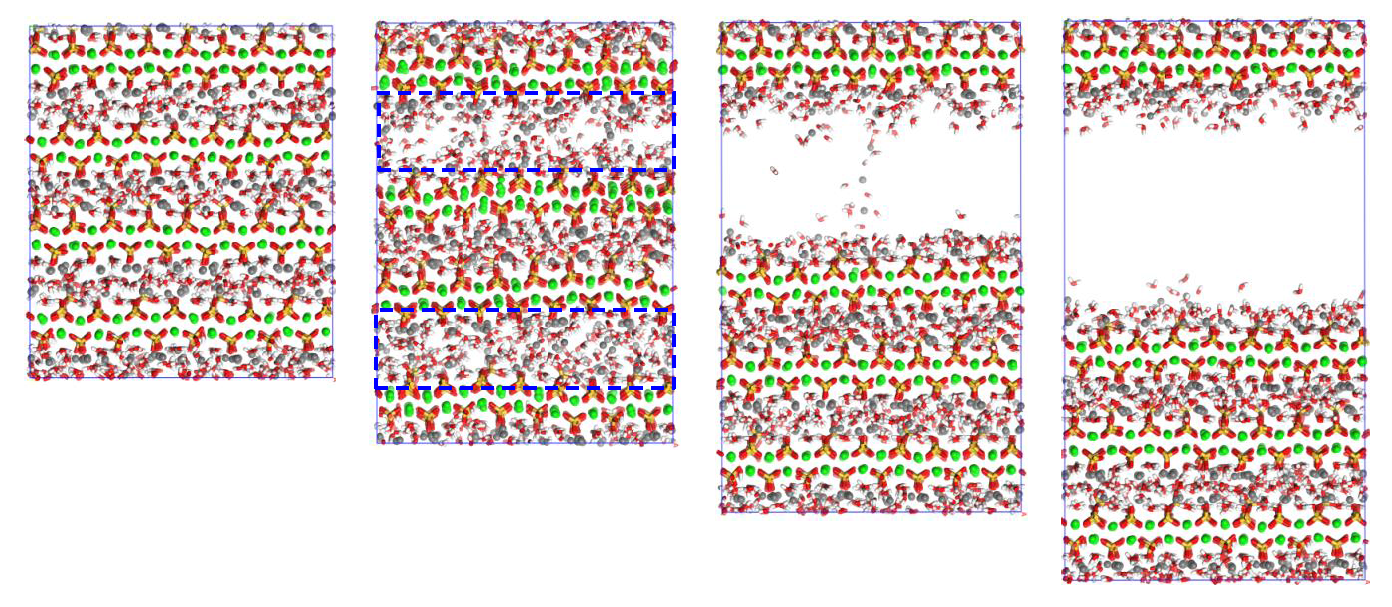
Figure 14. Molecular structure evolution (view along y direction) of C-S(-H) models with hydration degrees of 100% (first row) and 0% (second row) during z axial tensioning. The first, second, third and fourth columns are configurations at strains of 0.0, 0.2, 0.4 and 0.6 Å/Å, respectively.
论文得到了国家自然科学基金青年基金(5200802)、武汉理工大学硅酸盐建筑材料国家重点实验室开放课题(SYSJJ2022-22)资助,是该团队国内科研交流合作取得的重要成果。(文:肖必华图:杨军 审稿:丁益)

